Interpretation of Sequence Variants
Jun Kang
Geuess Pathogenic or Benign
Geuess Pathogenic or Benign

Question
- Can our lab classify novel missense variant into pathogenic or benign, not VUS?
Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants
- To describe variants identified in Mendelian disorders
- American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)
- ENIGMA BRCA1/2 Gene Variant Classification Criteria
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
Why is BRCA1/2 special?
- High prevalence in population
- Frequent benign variant
What about hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOCS)
- BRCA1/2 and other genes
- Breast, ovarian cancer and other cancers
- Prevalence (between 1 in 400 to 1 in 800 people)
- Penetration rate (40-90%)
Categories of interpretation of variants
- Pathogenic
- Likely-pathogenic
- Uncertain (VUS)
- Likely-benign
- Benign
Let's guess the evidences
Famly pedigree

Segregation data (BS1, PP1)
- Caveat: linkage disequilibrium
- Penetration rate
- Difficult statistical evaluation
Population data

Population data
- 5%: benign stand alone (BA1)
- 0.5-5% (BS1)
- Wow! The first time observed variant! (Absent in population DB, PM2)
Null variant
- Frameshift, Nonsense, canonical +-1 or 2 splicing site, initiation codon
- Caveat: LOF variants at the extreme 3′ end of a gene
- Caveat: presence of multiple transcripts
Computational (in silico) data
- PolyPhen2, SIFT, MutationTaster, etc
- Mutational hot spot and/or critical and wellestablished (PM1)
- Protein length changes due to in-frame deletions/insertions and stop losses functional domain (PM4 BP3)
- Novel missense at the same position (PM5)
Other evidence
- de novo variants (PS2 PM6)
- Functional studies (PS3 BS3)
- Allelic data (BP2 PM3)
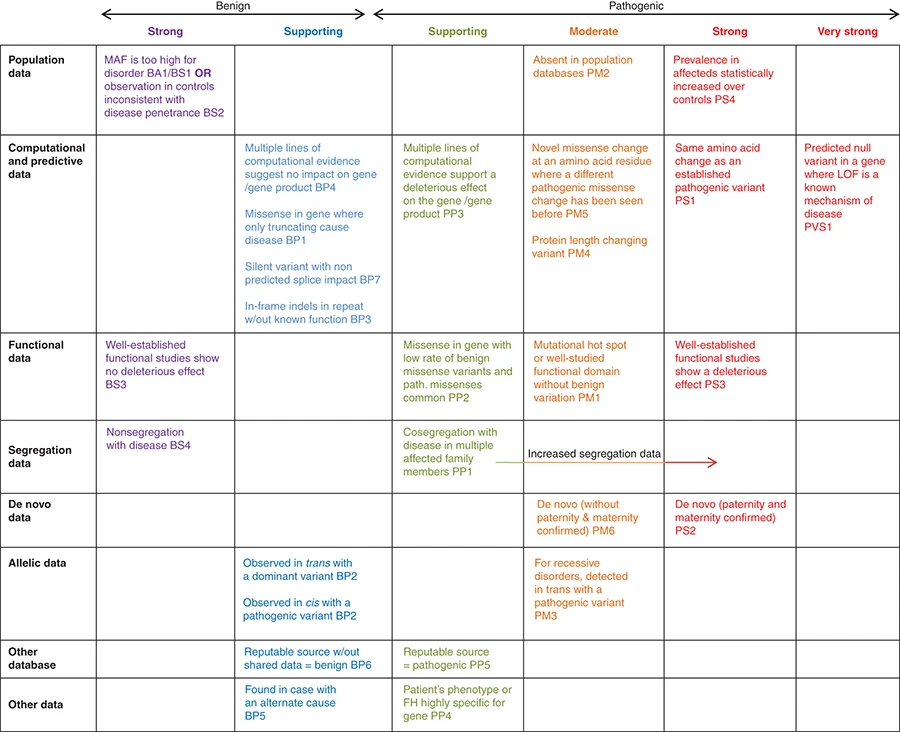
Evidences of interpretation
- Population data
- Computational data
- Functional data
- Segregation data
- De novo data
- Allele data
- Other databases
- Other data
27 variant attributes
Rules for combining criteria to classify sequence variants

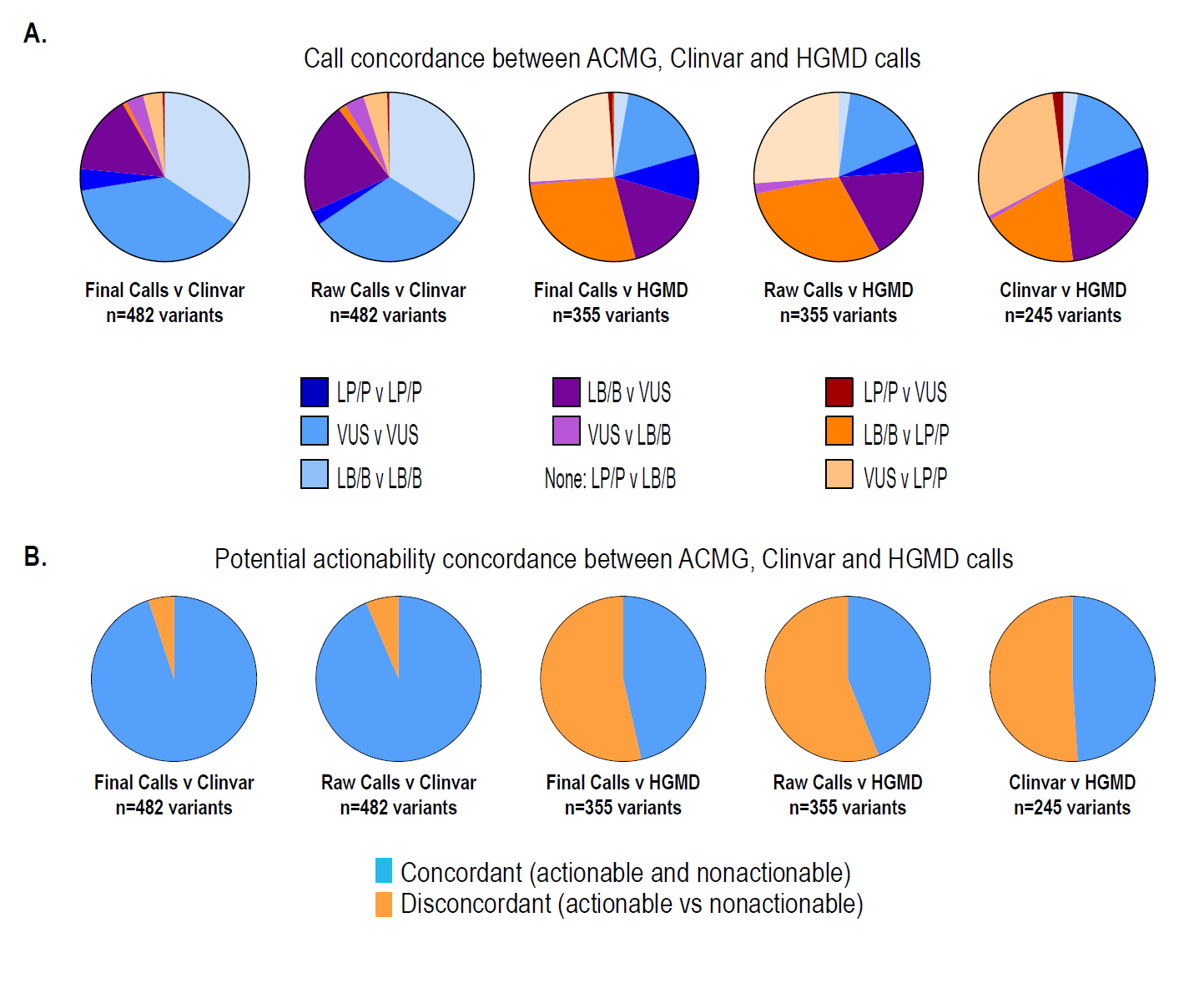
Evaluation of ACMG-Guideline-Based Variant Classification of Cancer Susceptibility and Non-Cancer-Associated Genes in Families Affected by Breast Cancer[1]
- Whole-exome sequencing
- 180 medically relevant genes
- 404 individuals
- 253 families
- 1,640 variants
Example (VUS)
- 76/M, Lung adenocarcinoma
- NM_000059.3(BRCA2):c.5683G>A (p.Glu1895Lys)
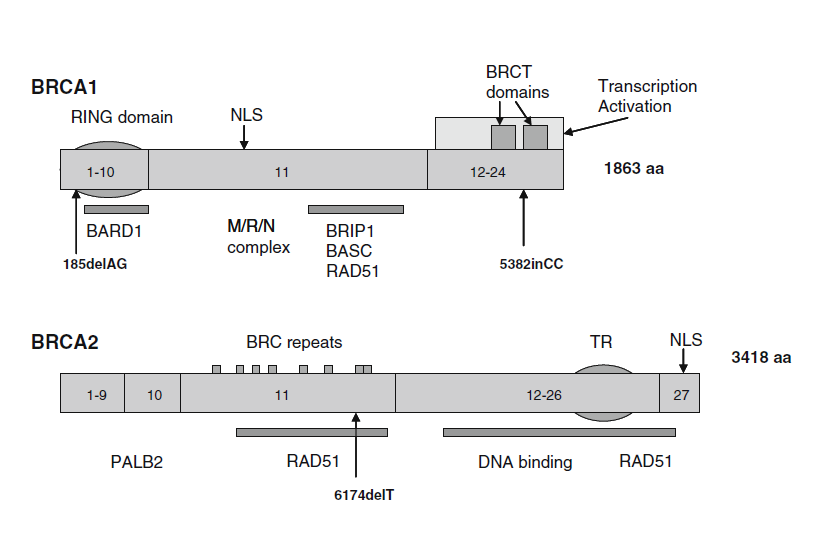
Characteristics of BRCA1/2
- LOF known mechanism of disease (for PVS1)
- Mode of inheritance (for PM3/BP2)
- AD/AR (BRCA2)
- Missense pathogenic (for PP2/BP1)
- BRCA2 1%
- Hot spot or critical/well-established functional domain (for PM1)
- BRCA2, Helical (2479-2667), OB (2670-2799 and 3052-3190), Tower (2831-2872)
NM_000059.3(BRCA2):c.5683G>A (p.Glu1895Lys)
- LOF known mechanism of disease (for PVS1)
- Mode of inheritance (for PM3/BP2)
- AD/AR (BRCA2)
- Missense pathogenic (for PP2/BP1)
- BRCA2 1%
- Hot spot or critical/well-established functional domain (for PM1)
- BRCA2, Helical (2479-2667), OB (2670-2799 and 3052-3190), Tower (2831-2872)
Characteristics of varant (NM_000059.3(BRCA2):c.5683G>A (p.Glu1895Lys))
- ClinVar (Uncertain significance (Last evaluated: Nov 1, 2015)) (PP5, BP6)
- Population AF: 8.29e−06 (PM2, BA1, BS1)
- Insilico SIFT 1.0, phyloP -0.72, PolyPhen-2 0.004 BP4
Functional assay (BS3)
- Findlay (2018) Nature 562: 217 PubMed: 30209399
- Guidugli (2013) Cancer Res 73: 265 PubMed: 23108138
- Biswas (2011) Blood 118: 2430 PubMed: 21719596
- Becker (2012) Breast Cancer Res Treat 135: 167 PubMed: 22729890
Summary
- Likely benign
- ≥ 2 supporting (BP1, BP4)
In Maxwell study [1]
Korean founder mutation BRCA1 p.Leu1780Pro
- 745 HBOC patients
- 86 VUS
- 64 missense
Korean founder mutation BRCA1 p.Leu1780Pro
- BRCA1 NM_007294.3:c.5339T>C Leu1780Pro
- No of patients: 11
- PS4: Odds ratio by Korean 41.2 (2.4-699.5)
- PS3: Functional study
- PP3: In silico test
- BP1: Missense
Question
Can our lab classify novel missense variant into pathogenic or benign, not VUS?
Answer
Yes, we can but...
Unrobust result
- BP4 (How many in silico test)
HBOC cohort
Experience
This sequence change replaces glutamic acid with lysine at codon 1895 of the BRCA2 protein (p.Glu1895Lys). The glutamic acid residue is weakly conserved and there is a small physicochemical difference between glutamic acid and lysine. This variant is present in population databases (rs146351301, ExAC 0.009%). This variant has been reported in individuals affected with breast cancer (PMID: 25682074, 20104584, 27257965, 28664449). In the literature, this variant is also known as 5911G>A. ClinVar contains an entry for this variant (Variation ID: 142307). Algorithms developed to predict the effect of missense changes on protein structure and function output the following: SIFT: "Tolerated"; PolyPhen-2: "Benign"; Align-GVGD: "Class C0". The lysine amino acid residue is found in multiple mammalian species, suggesting that this missense change does not adversely affect protein function. These predictions have not been confirmed by published functional studies and their clinical significance is uncertain. In summary, the available evidence is currently insufficient to determine the role of this variant in disease. Therefore, it has been classified as a Variant of Uncertain Significance.
Sherloc: a comprehensive refinement of the ACMG–AMP variant classification criteria [2]
- Iterative refinement of ACMG guideline
- 33 ACMG criteria to 108 criteria
- Combination of evidence to semiquantitative system
Challenges and Considerations in Sequence Variant Interpretation for Mendelian Disorders [3]
CMC pathology lab
- In house database
- https://brcaexchange.org/
- http://coda.nih.go.kr/coda/KRGDB/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/
- https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/
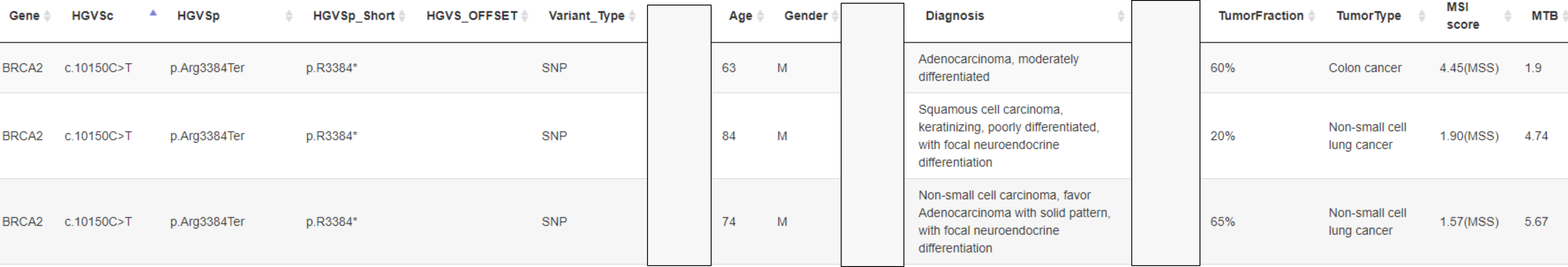
BRCA2 c.10150C>T p.Arf3384Ter
KOBRA [4]

End truncation
HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief 31: E 1200-E1240 (2010) Online
Finally, three sequence variants – BRCA2 c.9976A>T (BIC: K3326X), c.10095delCins11 (BIC: 10323delCins11) and c.10150C>T (BIC: R3384X) predicted to result in protein truncation were ruled as exceptions that could not be classified because of their location near the 3´-end and possibly dispensable part of the gene.
Clinvar
BRCA2 c.9976A>T (p.Lys3326*) variant, located upstream of this variant and also in the last exon of the gene, is a known benign variant.
Conclusions
- ACMG guideline
- Systemaic review system is requred
- Let's determine VUS to benign or even pathogenic
References
[1] K. Maxwell, S. Hart, J. Vijai, et al. "Evaluation of ACMG-Guideline-Based Variant Classification of Cancer Susceptibility and Non-Cancer-Associated Genes in Families Affected by Breast Cancer". In: The American Journal of Human Genetics 98.5 (5. 2016), pp. 801-817. ISSN: 0002-9297.
[2] K. Nykamp, M. Anderson, M. Powers, et al. "Sherloc: a comprehensive
refinement of the ACMG
[3] Y. Kim, C. Ki, and M. Jang. "Challenges and Considerations in Sequence Variant Interpretation for Mendelian Disorders". In: Annals of Laboratory Medicine 39.5 (9. 2019), pp. 421-429. ISSN: 2234-3806.
[4] E. Kang, M. Seong, S. K. Park, et al. "The prevalence and spectrum of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in Korean population: recent update of the Korean Hereditary Breast Cancer (KOHBRA) study". En. In: Breast Cancer Res Treat 151.1 (5. 2015), pp. 157-168. ISSN: 1573-7217.